Lenders use your credit score to assess your riskiness as a borrower. Higher credit scores indicate you are a responsible borrower and tend to lead to better loan terms and greater access to financial products. On the other hand, lower credit scores are a red flag for lenders and may lead to higher interest rates and even denied loans.
If your credit score ranges between 580-669, your score falls under the fair credit score range. But, what is a fair credit score and is it bad? To give you a better understanding of how fair credit stacks up to other credit score ranges, we’ll go over what fair credit is, how it impacts your financial life, and ways you can boost your credit.
Key Takeaways
- Credit scores fall into 5 ranges: excellent/exceptional, very good, good, fair, and poor.
- You will get different financial product offerings and rates depending on where your credit scores fall. Consumers with excellent credit typically get the best offerings and rates, lower insurance premiums, more rental options, and a greater likelihood of employment.
- There are 6 steps you can take to build your credit score from fair to good (and eventually excellent), including creating a budget, lowering your credit utilization ratio, making on-time payments, and more.
Credit Scores Ranges Explained
Currently, most credit scores range from 300-850 points, though some industry-specific models, such as auto loans, may range from 250-900. FICO credit scores fall within one of 5 ranges:
- Excellent/Exceptional (800–850): Borrowers with excellent credit scores often qualify for the best product offerings and terms.
- Very Good (740–799): Borrowers in this range have above-average credit scores and typically qualify for loans with favorable rates.
- Good (670–739): The average credit score falls under this category. Lenders are usually willing to approve loan applications for borrowers with good credit because they have a proven track record of repayment.
- Fair (580–669): Consumers with fair credit scores fall below average, but lenders may still approve their applications. However, they may have limited options and higher interest rates.
- Poor (300–579): Lenders typically turn down applicants with poor credit or may attach unfavorable terms if their applications get approved.
While fair credit and good credit are right next to each other on the credit scoring model, your financial offerings are much more favorable once you have a credit score above 670. You will be more likely to get approved for credit cards with more robust rewards programs and lower interest rates. Additionally, you will have more options when applying for an auto loan, personal loan, mortgage, or other loans.
Understanding Fair Credit Scores
According to Experian, the average American had a credit score of 714 points in 2022, which falls under good credit and is on the higher end of the credit-scoring spectrum. On the other hand, fair credit scores are often described as an “average credit score” and fall somewhere in the middle.
In other words, if you have a fair credit score, it is neither good nor bad. But, because fair credit is below average compared to other consumers, lenders generally view you as a medium to high risk borrower. That means it will be more difficult for you to get approved for loans, and if you do get approved, you may have worse terms than people with good to excellent credit.
Note that lenders may define fair credit differently and use many credit-scoring models. For example, FICO generally defines fair credit as scores ranging from the upper 500s to mid-600s, while Fair VantageScore defines fair credit as scores ranging in the low- to mid-600s.
While you may not always get the best loan terms, having a fair credit score is not the end of the world. Consider it as a stepping stone to getting to a good credit score range. Don’t forget that lenders will look at other factors, such as your ability to repay debt and debt-to-income ratio, when reviewing your loan application.
Breaking Down Your Credit Score
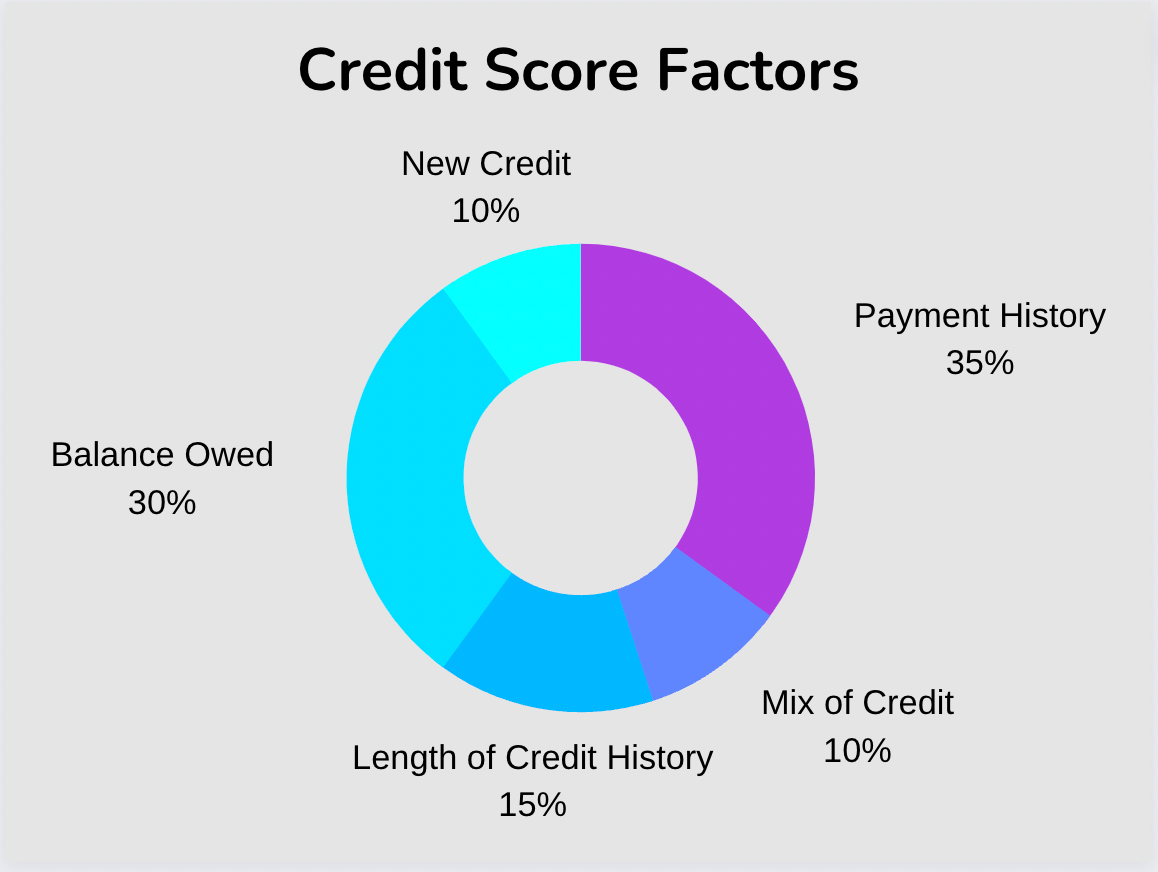
Your credit score is based on information in your credit report, which includes factors such as how much debt you have, how long you’ve had credit accounts open, and whether you’ve missed any payments.
The most important factor in calculating your credit score is your payment history. Late or missed payments can seriously hurt your score, while on-time payments can improve it. Your credit utilization ratio, or the percentage of your total available credit used, also plays a large role. Having too much debt can make it difficult to borrow money at favorable rates. Other factors include the average age of your credit accounts, your credit mix, and new credit.
The Benefits of Having Good Credit Scores
If you don’t have the best credit, the good news is that you’ll have plenty of opportunities to build up your credit. The amount of time it will take to move your credit from fair to good depends on where your credit score is currently, the types of negative information on your credit reports, and the steps you take to move your score up.
There are many benefits to having a good credit score, including:
- Better offers on financial products: Credit card companies typically reserve the best loan terms and product offerings for people with excellent credit because they have a proven track record of using credit responsibly. With a higher credit score, you will have a better chance of getting favorable terms for top-notch rewards credit cards. You will also be more likely to qualify for lower interest rates on personal loans, auto loans, mortgages, and other types of loans.
- Lower insurance premiums: People with higher credit scores tend to have lower insurance premiums. Depending on the state, insurance carriers may use credit-based insurance scores to determine insurance premiums. If you have excellent credit, you could save anywhere from 29-50% compared to consumers with no credit.
- More rental options: If you are in the market for a new apartment or house to rent, your future landlord may ask you to fill out an application to run a background check on you. The background check may include a credit check to vet your ability to pay rent. Depending on the rules of the state you live in, a landlord may deny your application if you have a shaky credit history.
- Greater likelihood of employment: While your future employer cannot check your credit score directly, depending on the job you are applying for, they may review an abbreviated version of your credit report to check your identifying information, payment history, and debt. If you have bad credit, employers have a right to deny you a job. But, they need your permission to conduct a credit check and are legally obligated to tell you if that influenced their decision to reject your application.
6 Ways to Improve Fair Credit
If you have a fair credit score, there are several steps you can take to improve your credit:
1. Create a Budget
The first step to a healthy financial life is to create a budget that works for you. By tracking where all your money is going, you can take charge of your finances and build a strong foundation. Take a look at your expenses from the last few months and identify the general areas where you are spending your money, such as rent, groceries, utilities, entertainment, etc. If you have a lot of debt or frequently overspend, find ways to lower your expenses to a more manageable amount.
Before I started budgeting, I had no idea where my money was going every month. After (obsessively) analyzing my spending habits using Mint and spreadsheets, I realized I was spending a lot of money on purchases that didn’t make me happy. By reassessing my lifestyle, I cut down on a lot of miscellaneous expenses, including clothes and shoes, that were not adding value to my life. That lowered my credit utilization and made it easier for me to pay off my credit card balances, which in turn boosted my credit scores.

2. Spread Credit Card Applications Out
Whenever you apply for a loan, the lender will check your credit reports by pulling a hard inquiry. Each hard inquiry can result in a 2-5 point drop in your credit score. If you apply for multiple credit cards simultaneously or apply for too many cards in a short timeframe, that can seriously damage your credit score.
If you have several credit cards you are eyeing, space out your applications and only apply once every 4-6 months to avoid having too many hard inquiries on your credit report. I spaced my last couple of credit card applications out a year apart to give myself enough time to meet the minimum spending requirements for the welcome bonuses and minimize the impact on my credit score.
3. Pay on Time and Reduce Debt
We recommend making on-time payments in full every month for your balances if you can. Even one late or missed payment can cause your credit score to take a hit, not to mention the late fee charges and higher interest rates. If you have multiple existing debts you need to pay off, tackle the ones with the highest interest rates first. By targeting the highest-impact balances early on, you can avoid your debt snowballing to an unmanageable amount.
4. Reduce Your Credit Utilization
If you can only afford to make the minimum payment or tend to max out your credit limit, that keeps your credit utilization ratio high, which hurts your credit. Experts generally recommend keeping your utilization ratio below 30% to indicate your creditworthiness to lenders, though the lower, the better. I typically keep mine under 10-15% to be safe. If you have a low credit limit, consider paying off your balance before the billing cycle ends. In the past, I have paid off my balance multiple times in the same billing cycle to lower my utilization ratio.
5. Increase Your Credit Limit
If keeping your credit utilization ratio low is an issue, an alternative is to increase your total available credit by requesting a credit limit increase from an existing card issuer or applying for a new credit card. If you have more credit available and can avoid overspending, your credit utilization will go down, and your credit score should increase.
When requesting a credit limit increase from your lender, ask them if they can pull a soft inquiry on your credit rather than a hard inquiry. With a soft credit pull, your credit score will not get impacted. Most credit card companies automatically raise your credit limit over time once you establish a solid payment history with them. Over the years, my credit limit has gradually increased as my income rose and payment history grew longer.

6. Check Your Credit Reports for Errors
You should pull your credit reports regularly from all three major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion). You are entitled to a free report every year by going to AnnualCreditReport.com.
Once you pull your credit reports, check the information thoroughly for any errors or mistakes. If you see anything inaccurate or unfamiliar, you should file a formal dispute with the respective credit bureau immediately and request to have the errors removed.
The Bottom Line
If your credit scores currently fall in the fair or poor range, there’s no need to panic. There are steps you can take to get to the good credit score category and bring your credit to the next level. As you build healthy financial habits by making on-time payments every month, keeping your credit utilization low, and budgeting accordingly, you should see your credit scores improve over time.

